Difference between revisions of "Second-order Material Characterization"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<br clear='all'> | <br clear='all'> | ||
[[Teng-Mann Method for Measuring Electro-optic coefficient]] | |||
<table id="toc" style="width: 100%"> | <table id="toc" style="width: 100%"> | ||
Revision as of 09:30, 1 October 2009
| Previous Topic | Return to Second-order Processes, Materials & Characterization Menu |
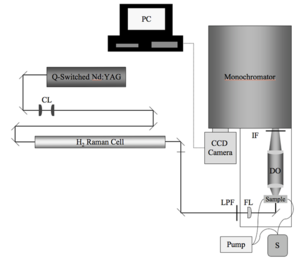
Characterization
β, the first nonlinear polarizability depends on molecular structure, environment and measurement frequency. There are several tools that help us characterize the materials.
Hyper Rayleigh Scattering (HRS)
Hyper Rayleigh Scattering (aka Harmonic Light Scattering) is one method for measuring β.
An incident laser generates a second harmonic signal, specifically the frequency double signal. This can be related to the beta of the sample using this formula:
- <math>\frac {I_{sample}} {I_{solvent}} = \frac {N_{sample} \langle \beta^2 _{sample} \rangle + N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle} {N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle}\,\!</math>
See Firestone 2004 [1].
See also Density Functional Theory
Teng-Mann Method for Measuring Electro-optic coefficient
| Previous Topic | Return to Second-order Processes, Materials & Characterization Menu |
- ↑ K. A. Firestone, P. Reid, R. Lawson, S. H. Jang, and L. R. Dalton, “Advances in Organic Electro-Optic Materials and Processing,” Inorg. Chem. Acta, 357, 3957-66 (2004)