Difference between revisions of "Hyper Rayleigh Scattering"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
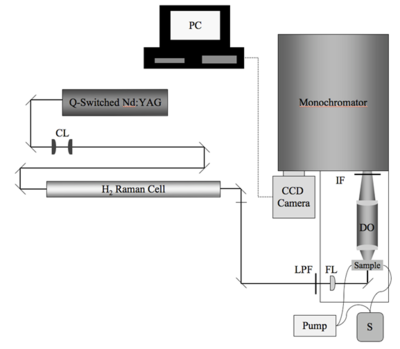
[[Image:Hrs.png|thumb|400px|Schematic of the HRS setup. CL = collimating lenses; LPF = long-pass filter; FL = 300-mm focusing lens; S = solution of chromophore in solvent of choice; DO = detection optics; IF = interference filter (950 nm)]] | [[Image:Hrs.png|thumb|400px|Schematic of the HRS setup. CL = collimating lenses; LPF = long-pass filter; FL = 300-mm focusing lens; S = solution of chromophore in solvent of choice; DO = detection optics; IF = interference filter (950 nm)]] | ||
A dilute sample of test chromophore is prepared in a solvent. The | In HRS A dilute sample of a test chromophore is prepared in a solvent. The dielectric properties of the solvent influence the β (solvatochromatism). | ||
In HRS | In HRS An incident laser generates a second harmonic signal, specifically the frequency double signal. This can be related to the beta of the sample using this formula: | ||
:<math>\frac {I_{sample}} {I_{solvent}} = \frac {N_{sample} \langle \beta^2 _{sample} \rangle + N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle} {N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle}\,\!</math> | :<math>\frac {I_{sample}} {I_{solvent}} = \frac {N_{sample} \langle \beta^2 _{sample} \rangle + N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle} {N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle}\,\!</math> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
See also [[Density Functional Theory]] | See also [[Density Functional Theory]] | ||
See Wikipedia on [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raman_scattering Raman Scattering] | |||
=== Technique === | === Technique === | ||
Video to come | Video to come | ||
=== Significance === | === Significance === | ||
Revision as of 12:21, 12 October 2009
Hyper Rayleigh Scattering (aka Harmonic Light Scattering or HRS) is one method for measuring the first hyperpolarizabilityβ. Another method is electric field induced second harmonic generation (EFISH)
Overview
In HRS A dilute sample of a test chromophore is prepared in a solvent. The dielectric properties of the solvent influence the β (solvatochromatism). In HRS An incident laser generates a second harmonic signal, specifically the frequency double signal. This can be related to the beta of the sample using this formula:
- <math>\frac {I_{sample}} {I_{solvent}} = \frac {N_{sample} \langle \beta^2 _{sample} \rangle + N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle} {N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle}\,\!</math>
See Firestone 2004 [1].
See Wikipedia on Rayleigh Scattering
See also Density Functional Theory
See Wikipedia on Raman Scattering
Technique
Video to come
Significance
References
- ↑ K. A. Firestone, P. Reid, R. Lawson, S. H. Jang, and L. R. Dalton, “Advances in Organic Electro-Optic Materials and Processing,” Inorg. Chem. Acta, 357, 3957-66 (2004)